SOCIAL MEDIA
Portuguese Medical Association's Scientific Journal
Introduction: Screening is effective in reducing cancer-related morbidity and mortality. The aim of this study was to analyze the level of, and income-related inequalities in, screening attendance, in Portugal for population-based screening programs.
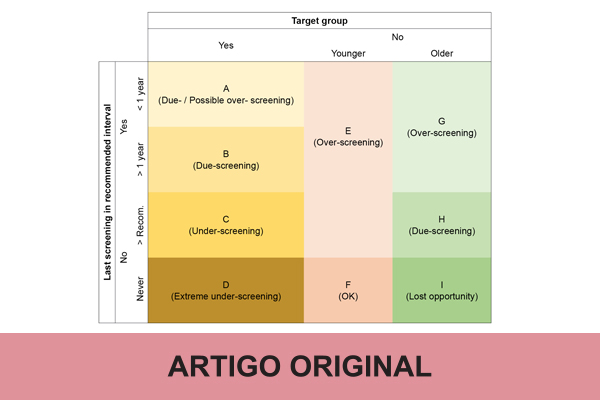
Methods: Data from the Portuguese Health Interview Survey 2019 was used. Variables included in the analysis were self-reported: mammography, pap smear test, fecal occult blood test. Prevalence and concentration indices were computed at national/regional level. We analyzed: up-to-date screening (within recommended age/interval), under-screening (never or overdue screening), and over-screening (due to frequency higher than recommended or screening outside target group).
Results: Up-to-date screening rates were 81.1%, 72%, and 40%, for breast, cervical and colorectal cancer, respectively. Never-screening was 3.4%, 15.7%, and 39.9%, for breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer, respectively. Over-screening related with frequency was highest for cervical cancer; in breast cancer, over-screening was observed outside recommended age, affecting one third of younger women and one fourth of older women. In these cancers, over-screening was concentrated among women with higher income. Never-screening was concentrated among individuals with lower income for cervical cancer and higher income for colorectal cancer. Beyond the recommended age, 50% of individuals never underwent screening for colorectal cancer and 41% of women never underwent screening for cervical cancer.
Conclusion: Overall, screening attendance was high, and inequalities were low in the case of breast cancer screening. The priority for colorectal cancer should be to increase screening attendance.